Anti-IgD Nanobodies as Novel Tools for Studying Human IgD Biology
While immunoglobulin D (IgD) was one of the earliest antibody isotypes to be discovered, its biological function remains the most enigmatic. Despite being co-expressed with IgM on naïve B cells and implicated in immune surveillance, IgD has been historically underexplored—largely due to the lack of reliable tools for its detection and functional analysis.
At AlpalifeBio, we believe that robust, specific tools are key to unlocking biological insights. In this study, we report the development and characterization of four anti-human IgD nanobodies (VHHs) that offer high specificity and versatility for both basic research and translational applications.
Why Nanobodies for IgD?
Nanobodies—single-domain antibodies derived from camelids—are gaining ground as powerful tools for biochemical and cellular research. Their small size, high affinity, and ease of engineering make them ideal for applications such as protein purification, imaging, diagnostics, and therapeutic development.
In the case of IgD, nanobody-based reagents overcome many of the limitations of traditional antibodies by offering:
High specificity to defined epitopes,
Stable performance under diverse experimental conditions,
Ease of genetic fusion to functional domains.
Characterizing the Anti-IgD Nanobody Panel
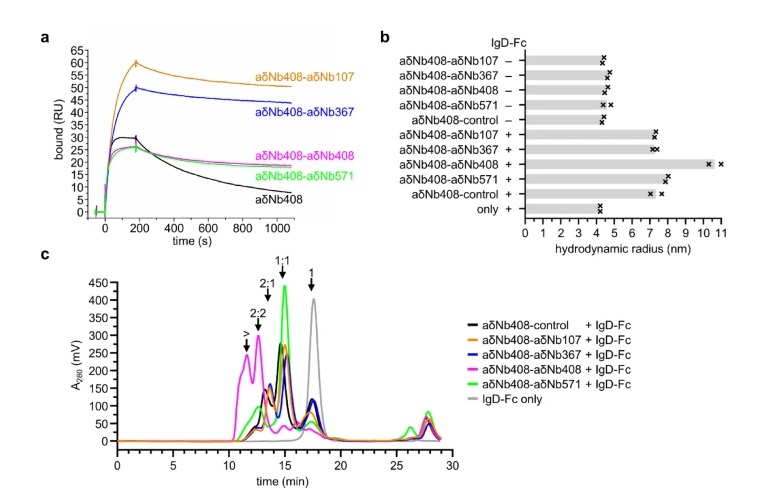
Our panel includes four nanobodies that bind specifically to the Fc region of human IgD with low nanomolar affinity. Each nanobody exhibits:
Unique binding kinetics,
Distinct epitope recognition, and
Different interaction stoichiometries.
One standout candidate, aδNb408, demonstrated excellent performance in IgD purification workflows, with high-efficiency capture and mild elution at pH 3.5—ideal for preserving IgD integrity and downstream activity.
Functional Tools for IgD Interaction Studies
To support real-time interaction studies via surface plasmon resonance (SPR), two nanobodies in our panel showed strong IgD capture capabilities. This makes them valuable tools for researchers investigating IgD-ligand or IgD-receptor dynamics.
Additionally, we explored nanobody multimerization strategies to enhance avidity:
Bivalent formats improved signal strength,
Bispecific combinations allowed simultaneous recognition of non-overlapping epitopes.
The aδNb408-aδNb107 bispecific nanobody enabled robust detection of IgD on Namalwa B cells, highlighting its potential as a cellular staining or diagnostic tool.
Applications & Future Directions
These anti-IgD nanobodies open the door to a wide range of experimental applications:
Affinity purification of native IgD,
Quantitative IgD detection in immunoassays,
SPR-based binding studies,
Cell surface staining in flow cytometry or microscopy,
And potentially, targeted delivery platforms in IgD-associated B cell research.
As our understanding of IgD biology grows, these tools will enable deeper exploration of its roles in immune regulation, mucosal defense, and B cell physiology.
About AlpalifeBio's Nanobody Platform
With a proprietary alpaca herd and 100% IP ownership model, AlpalifeBio delivers customized nanobody discovery services to support research, diagnostics, and therapeutic development. Our experienced team and advanced screening pipeline enable rapid development of high-quality nanobodies against even the most challenging targets.
If you're interested in working with nanobodies for rare or underexplored targets like IgD, we'd love to hear from you.
Contact us to explore custom nanobody solutions.
Source: Nature